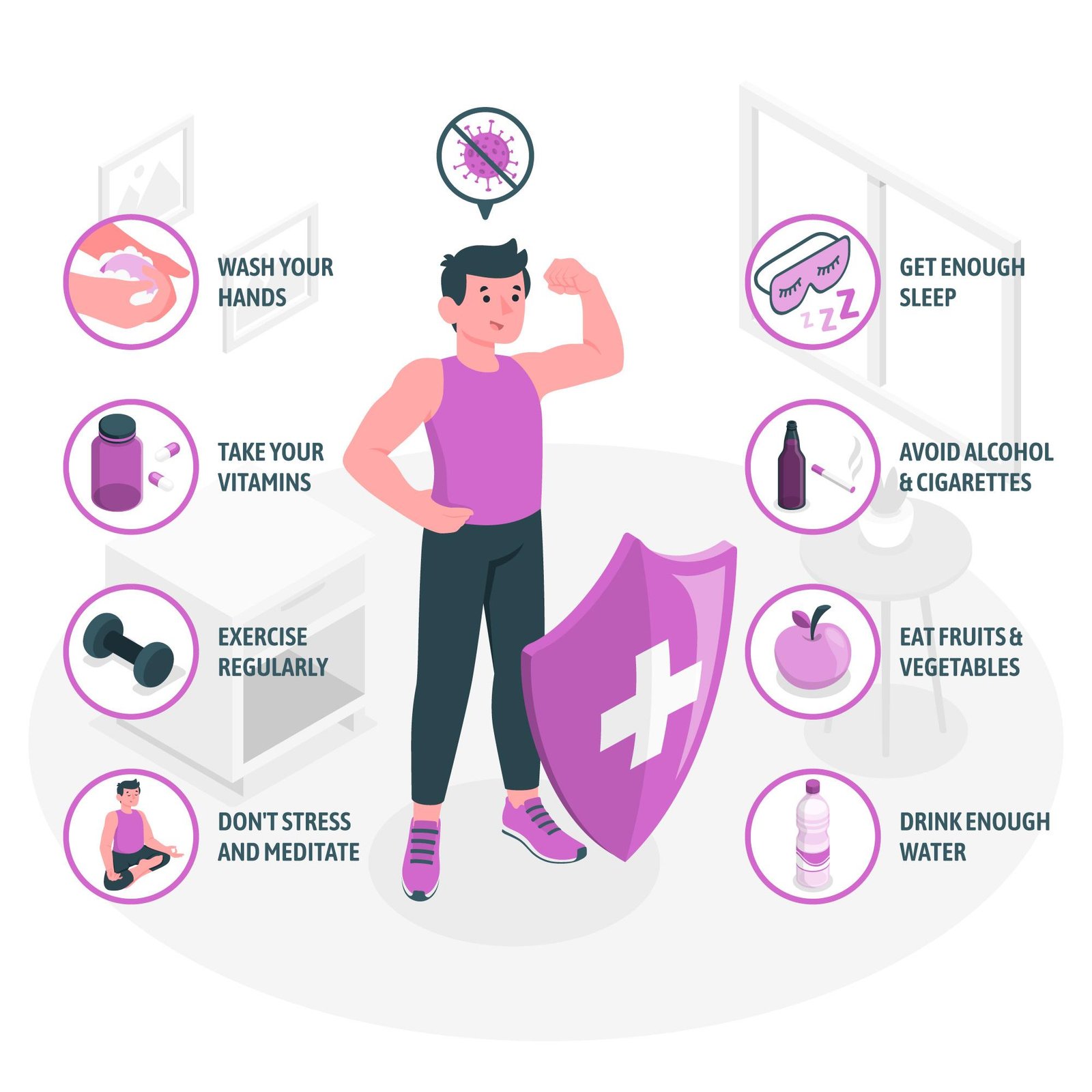
In the realm of healthcare, prevention is unequivocally preferred over treatment. Disease prevention not only saves lives but also reduces healthcare costs and improves the quality of life for individuals and communities. With the rise of chronic diseases alongside infectious diseases, understanding and implementing effective prevention strategies is paramount. This article explores the various methods of disease prevention, emphasizing the importance of lifestyle changes, preventive care, and community efforts in controlling and preventing diseases.
Understanding Disease Prevention
Disease prevention encompasses measures taken to prevent the onset of diseases, rather than curing them. It is typically divided into three categories: primary, secondary, and tertiary prevention. Primary prevention aims to prevent the disease before it occurs, secondary prevention focuses on early detection to halt or slow the progression of disease, and tertiary prevention seeks to reduce the impact of ongoing illness by softening its impact.
Primary Prevention Strategies
Regular Physical Activity
Engaging in regular physical activity is a cornerstone of disease prevention. Exercise strengthens the heart, improves blood circulation, and can help control body weight, reducing the risk of heart disease, diabetes, and many other chronic conditions.
Healthy Eating Habits
A balanced diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins can prevent a plethora of health issues. Nutrient-dense foods support overall health and help maintain a healthy weight, thereby reducing the risk of chronic diseases.
Personal Hygiene
Good personal hygiene practices, such as regular handwashing, can prevent the spread of infectious diseases. Personal hygiene plays a crucial role in preventing illnesses like the flu, colds, and other communicable diseases.
Vaccination
Vaccines are one of the most effective ways to prevent diseases. They protect against conditions such as measles, polio, and hepatitis. The Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) recommends vaccinations from early childhood through adulthood to provide a lifetime of protection against many diseases.
Secondary Prevention Measures
Regular Screenings and Check-ups
Regular health screenings for blood pressure, cholesterol levels, diabetes, and cancer can detect diseases at an early stage, where they are more treatable. Early detection through screenings is vital for controlling and preventing the progression of chronic diseases.
Monitoring Risk Factors
Identifying and monitoring risk factors such as high blood pressure and cholesterol can help prevent diseases like heart disease and stroke. Lifestyle modifications and medications, when necessary, can control these risk factors effectively.
Tertiary Prevention Efforts
Chronic Disease Management
For individuals with chronic diseases, managing the condition to prevent complications is a form of tertiary prevention. This includes following treatment plans, taking prescribed medications, and regular monitoring and self-care practices to manage the disease effectively.
Rehabilitation
Rehabilitation services for conditions such as stroke or heart attack aim to help individuals regain strength, recover as much function as possible, and return to daily activities. This form of prevention works to minimize the impact of the disease on the individual’s health and quality of life.
Prevention Health Promotion
Educating the Public
Education plays a crucial role in disease prevention and health promotion. Awareness campaigns and health education teach the public about the importance of preventive measures, how to recognize the signs and symptoms of diseases, and when to seek medical help.
Community Health Initiatives
Community health initiatives can address environmental and social factors that contribute to diseases. These may include programs to increase access to healthy foods, improve air and water quality, and provide safe spaces for physical activity.
Preventive Care and Regular Check-ups
Preventive care, including regular check-ups with healthcare providers, is essential for maintaining good health and preventing diseases. These visits allow for early detection of risk factors or the early stages of diseases, leading to more effective management and outcomes.
Vaccination: A Cornerstone of Infectious Disease Prevention
Vaccination stands as one of the most effective methods of primary prevention against infectious diseases. By stimulating the body’s immune system to recognize and fight specific pathogens, vaccines prevent the onset of diseases such as measles, influenza, and human papillomavirus (HPV), which can lead to chronic health issues. Public health initiatives and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) emphasize the importance of vaccinations in disease control and prevention strategies, significantly reducing the prevalence of many communicable diseases and, in some cases, leading to their eradication.
Nutritional Interventions for Chronic Disease Prevention
A balanced diet plays a critical role in the prevention of chronic diseases, including heart disease, diabetes, and certain cancers. Nutritional interventions focus on promoting a diet rich in fruits, vegetables, whole grains, and lean proteins while limiting the intake of processed foods, sugars, and saturated fats. These dietary practices can help manage risk factors such as high blood pressure and obesity, thus preventing the onset of chronic conditions. Health promotion efforts often include educational campaigns and policies aimed at increasing access to healthy food options and encouraging individuals to make informed nutritional choices.
Environmental and Occupational Health Measures
Environmental and occupational health measures focus on reducing exposure to hazardous substances and conditions that can lead to diseases. This includes implementing regulations to control air and water pollution, ensuring safe handling of toxic materials, and enforcing safety standards in the workplace. By controlling these environmental and occupational risk factors, it is possible to prevent a wide range of diseases, from respiratory illnesses caused by air pollution to occupational cancers resulting from long-term exposure to hazardous chemicals. These preventive strategies require collaboration between governments, industries, and communities to create safer environments for all.
Stress Management and Mental Health Promotion
Stress management and mental health promotion are crucial components of disease prevention, addressing the psychological factors that contribute to physical health conditions, including heart disease and chronic illnesses. Implementing strategies such as mindfulness, meditation, and counseling can significantly reduce stress levels, improving overall well-being. Encouraging regular mental health check-ups and creating awareness about the importance of mental health are vital in prevention health promotion. By addressing mental health as part of a holistic approach to disease prevention, individuals can improve their quality of life and reduce the risk of stress-related diseases.
Regular Screening and Early Detection
Regular screening and early detection are key strategies in the secondary prevention of diseases. These methods aim to identify and treat conditions in their early stages before they develop into more serious health issues. Screenings such as mammograms, colonoscopies, and blood pressure checks can detect risk factors or early signs of diseases like cancer, heart disease, and hypertension. By promoting and providing access to regular screenings, healthcare providers can significantly lower the mortality and morbidity rates associated with chronic diseases and improve health outcomes for individuals and populations.
Promoting Physical Activity in Community Settings
Encouraging physical activity within communities through the development of parks, recreational facilities, and community programs is an effective method of disease prevention. Regular physical activity is proven to reduce the risk of chronic diseases such as heart disease, diabetes, and obesity. Creating environments that support active lifestyles, such as safe walking paths and community sports leagues, can foster regular physical engagement among people of all ages. Public health campaigns that promote the benefits of physical activity and provide opportunities for engagement can play a significant role in improving public health and preventing disease on a wide scale.
Stress Management and Mental Health Support
Effective stress management and robust mental health support play crucial roles in disease prevention, particularly for chronic conditions like heart disease and diabetes, where stress is a known risk factor. Incorporating stress-reducing practices such as mindfulness, meditation, and regular physical activity can significantly lower stress levels, improving overall health. Additionally, access to mental health services and support for conditions like depression and anxiety is vital, as these can have a profound impact on physical health and the effectiveness of disease prevention strategies. Prioritizing mental wellness helps in the holistic prevention of diseases by addressing the psychological factors that contribute to physical health.
The Role of Regular Screenings and Check-ups
Regular health screenings and medical check-ups are essential components of secondary prevention. They allow for the early detection of diseases such as cancer, diabetes, and heart disease, often before symptoms arise. Early diagnosis can lead to more effective treatment, significantly increasing the chances of successful management and recovery. Health professionals and the Centers for Disease Control and Prevention advocate for regular screenings based on age, sex, and risk factors, emphasizing their importance in preventive health care and chronic disease management.
Community Education and Public Health Campaigns
Community education and public health campaigns are critical in promoting disease prevention methods and health promotion across populations. These campaigns can raise awareness about the importance of vaccinations, healthy lifestyle choices, and preventive measures against infectious and chronic diseases. By leveraging media, schools, and community centers, public health organizations can disseminate vital information on disease prevention and control, encouraging people to adopt healthier behaviors. Tailored educational programs can address specific community needs and cultural factors, enhancing the effectiveness of prevention strategies and facilitating better health outcomes.
Conclusion
The methods of disease prevention are multifaceted and require a combined effort from individuals, healthcare providers, and communities. By incorporating regular physical activity, maintaining a healthy diet, practicing personal hygiene, and participating in vaccination and regular screenings, individuals can significantly reduce their risk of chronic and infectious diseases. Moreover, education and community health initiatives play vital roles in promoting health and preventing diseases. Together, these strategies form a comprehensive approach to disease prevention, aiming to improve health, extend life expectancy, and enhance the quality of life for people worldwide.



