In the dynamic landscape of global health, effective disease control measures are paramount. These measures encompass a broad spectrum of strategies, from prevention and infection control to the promotion of healthy habits and public health initiatives. This comprehensive post explores various aspects of disease control, integrating essential LSI keywords such as disease, prevention, health, infection, infectious diseases, public health, and more, and providing insights into how these measures are implemented and their significance.
Understanding Disease Control and Prevention
The Critical Role of Centers for Disease Control and Prevention
Centers for Disease Control and Prevention (CDC) and similar entities worldwide are at the forefront of disease control. They provide crucial guidelines and strategies for disease prevention and control, focusing on managing infectious diseases and maintaining public health.
Standard Precautions in Infection Control
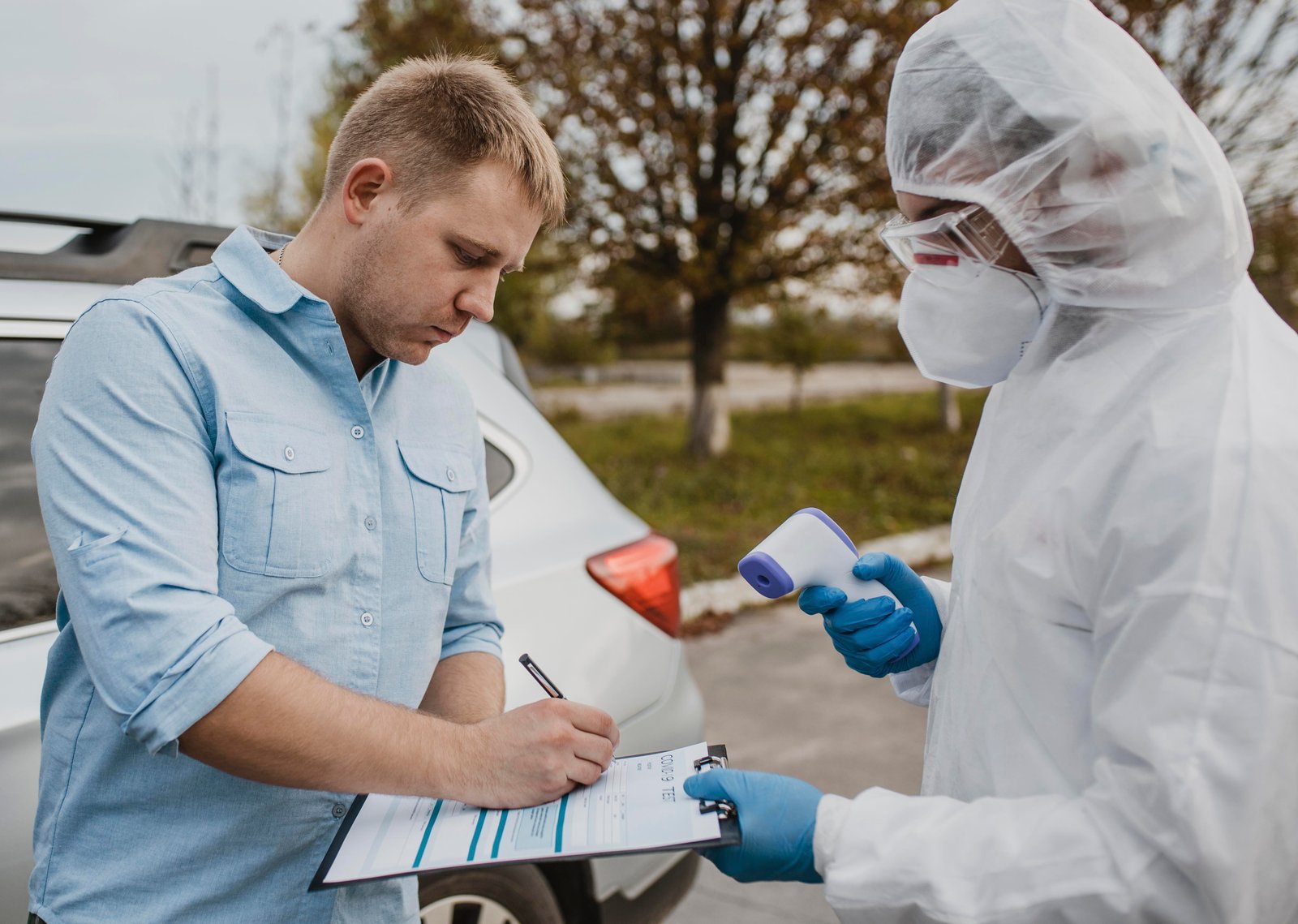
Standard precautions are the foundation of infection control. These include practices like proper hand hygiene, use of personal protective equipment (PPE), and adherence to sanitation protocols. Such measures are crucial in preventing the spread of infectious agents, not just in healthcare settings but also in public spaces.
Implementing Effective Disease Control Measures
Infection Prevention and Control Strategies
Effective infection prevention and control measures are key to halting the spread of diseases. This includes widespread vaccination campaigns, sterilization of medical equipment, and implementing quarantine protocols when necessary.
Public Health Surveillance and Disease Control
Public health surveillance is a critical aspect of disease control. By monitoring the spread of diseases, health authorities can take timely actions to mitigate risks. This data-driven approach is vital for early detection, prompt response, and the implementation of effective disease control measures.
Strategies for Disease Prevention
Encouraging Healthy Habits for Disease Prevention
Promoting healthy habits is essential in disease prevention. Habits such as maintaining a balanced diet, regular physical activity, and getting adequate sleep can significantly bolster the immune system, reducing the risk of contracting infectious diseases.
Vaccination: A Pillar of Disease Prevention
Vaccination is one of the most effective disease prevention strategies. It provides community-wide immunity against various infectious diseases, making it a cornerstone of public health initiatives.
The Global Role of the World Health Organization in Disease Control
Setting Global Standards for Disease Control
The World Health Organization (WHO) plays a pivotal role in establishing global standards for disease control and prevention. Their guidelines and protocols heavily influence health policies and practices across the world, ensuring a standardized approach to managing health crises.
Collaborative Health Promotion Efforts
The WHO works in collaboration with countries and international bodies to promote health and prevent diseases. These efforts include educational campaigns, research initiatives, and resource allocation for effective disease control.
Disease Control in Diverse Settings
Healthcare Settings and Infection Control
In healthcare environments, infection control measures are rigorously implemented. This includes the use of PPE, regular sanitization, and implementing isolation protocols for patients with infectious diseases.
Public Spaces and Disease Control Measures
In public settings, disease control measures like social distancing, mask-wearing, and promoting hand hygiene have become standard practices to control disease spread.
The Evolving Challenge of Infectious Diseases
Adapting to Changing Disease Dynamics
The nature of infectious diseases is constantly evolving, necessitating an adaptive approach to disease control and prevention. Ongoing research and the modification of strategies are essential to effectively manage new and emerging health threats.
The Importance of Community Involvement
Active community involvement is crucial for successful disease control and prevention. Public awareness and adherence to health guidelines play a significant role in mitigating the spread of diseases.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 4 steps of disease control?
Primordial, primary, secondary, and tertiary preventive stages are these stages of prevention. When combined, these tactics seek to reduce risk of disease development while also preventing complications that may arise from a disease that has already manifested.
What is disease prevention measures?
Primary prevention is defined as taking steps to prevent the onset of a disease. These steps can include modifying the way that social and economic determinants of health affect health, disseminating information about behavioral and medical health risks, and providing guidance.
What are the two main measures of disease?
Different goals and research questions are addressed by the use of prevalence and incidence. In this article, we go over the various disease frequency measures and explain which one to use when.
What is the difference between prevention and control of disease?
When we talk about prevention, we're talking about taking steps to stop an illness from happening. Control refers to actions taken to stop the disease from spreading after it has already started.
Conclusion
Disease control measures are vital in maintaining public health and safety. Through a deep understanding and implementation of various strategies, from infection prevention and control in healthcare settings to promoting healthy habits and robust public health surveillance, we can significantly mitigate the spread and impact of infectious diseases. The coordinated efforts of organizations like the CDC, WHO, healthcare professionals, and the general public are indispensable in the ongoing battle against infectious diseases. As we continue to face new health challenges, our collective response and adaptability will be the key to effective disease control and prevention.